Effects of Unexpected Chords and of Performer's Expression on Brain Responses and Electrodermal Activity
Sound Examples - here are examples of just one piano sonata (Beethoven
Piano Sonata F major Op 10 Nr 2), the entire corpus of stimuli
comprised excerpts from twenty-five piano sonatas.
(1) original excerpt with a slightly irregular chord played by a pianist
(2) original excerpt with a slightly irregular chord played without expression (by a computer)
(3) excerpt in which the original, slightly irregular chord was rendered regular, played by a pianist
(4) excerpt in which the original, slightly irregular chord was rendered regular, played without expression (by a computer)
If you had difficulties finding the slightly irregular chord in (1) and (2) try these:
(5) excerpt in which the original, slightly irregular chord was rendered very irregular, played by a pianist
(6) excerpt in which the original, slightly irregular chord was
rendered very irregular, played without expression (by a computer)
Here are examples of the scores:
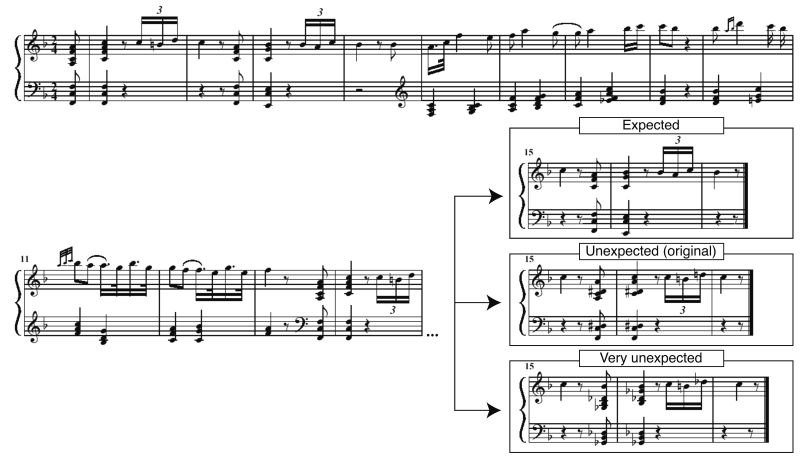
Download high-resolution image HERE.
Examples of experimental stimuli. First,
the original version of a piano sonata was played by a pianist. This
original version contained an unexpected chord as arranged by the
composer (see middle panel in the lower right). After the recording,
the MIDI file with the unexpected (original) chord was modified offline
using MIDI software so that the unexpected chord became expected, or
very unexpected chord (see top and bottom panels). From each of these
three versions, another version without musical expression was created
by eliminating variations in tempo and key-stroke velocities (excerpts
were modified offline using MIDI software). Thus, there were six
versions of each piano sonata: Versions with expected, unexpected, and
very unexpected chords, and each of these versions played with and
without musical expression.
